WHAT ARE INTERLEUKINS?
Interleukin is a sort of cytokine, which plays a critical role in immunological homeostasis and classification; it was discovered initially from leukocytes. Interleukins (IL) are cytokines that were first expressed by leukocytes alone but later produced by several different parts of body cells. Many cells currently generate it, including lymphocytic cells and macrophages with a solid structure and function.
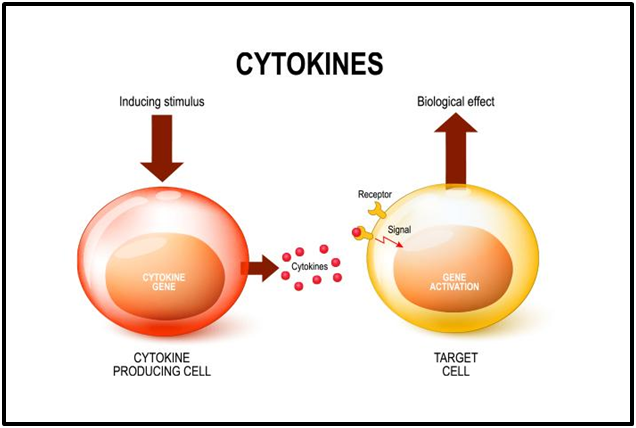
Cytokine proteins play essential roles in activating and differentiating immune cells and maturation, migration, proliferation and adhesion. They also possess anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties.
Therefore, accurate cytokine concentration detection and assessment become crucial for determining the characteristics of the infection and effective for monitoring the disease-staging process. To do this, scientists are increasingly using enzyme labels and immunoassays using enzyme-conjugated antibodies. The ELISA test is an ideal analytical tool that is commonly used by scientists for analysing antibodies, antigens, proteins and glycoproteins. Due to its many advantages, the ELISA principle is becoming more and more crucial in cytokine analysis.
At Helvetica Health Care, we provide a wide range of ELISA kits ready to use with break-apart wells. Our range of ELISA includes:
• The RETROTEK™ range is designed for the detection and quantitation of retroviral antigens from the retroviruses HIV-1, SIV and HTLV found in cell culture, serum, plasma or other biological fluids
• IMMUNOTEK™ kits can detect and quantify various immunoglobulins from many species, including Humans, Chicken, Cow, Goat, Rabbit, Rat and Mouse. We also provide HHV-6 IgG antibody and KSHV/HHV8 IgG antibody ELISA kits.
Therefore, the primary function of interleukins is to accentuate differentiation, growth, and activation throughout inflammatory and immune responses. Interleukins consist of many proteins that can elicit reactions in mast cells and tissues by binding to high-affinity receptors in cell exteriors. Interleukins are also used in animal researches to study characters associated with clinical medicine.
What are the general properties of Interleukins or Cytokines?
➔ Cytokines are proteins in response to pathogens and other antigens that regulate and mediate inflammatory and immune responses.
➔ Interleukin generation is a self-limited process; the messenger RNA encoding most interleukins is volatile, causing a brief synthesis and these molecules are rapidly concealed once synthesised.
➔ Up- and down-regulatory mechanisms include cellular responses to interleukins with the induction and participation of genes that encode inhibitors of the cytokine receptors.
➔ Interleukins have redundant purposes.
➔ Cytokines stimulate the activation of microbicidal mechanisms in phagocyte switching of antibody isotypes in B cells.
➔ Interleukins often affect other interleukin synthesis and actions.
➔ External signals or high-affinity receptors are stimulated and regulated by cellular responses to cytokines.
➔ Most cytokines act either on the same cell lines that secrete the cytokine; or may enter the circulation and act far from the production site.
➔ Small masses of a cytokine are required to seize receptors and extract biological conclusions.
What are the types of Interleukins and their functions?
Interleukin is essential for transmitting information, activating and regulating immune cells, propitiates the cell activation, proliferation and differentiation of T cells and B cells. Interleukin-1 contains IL-1α and IL-1β. While the former is produced by diverse cells, some specific tissues have the latter one.
IL-1β is cleaved by caspase-1, which is formed by proteins termed as the inflammasome. While the IL-1 receptor antagonist can inhibit the destruction of IL-1 through the completion of the same receptor, it can lead to pain and short-time sleep to study the association between fatigue and IL-1. IL-1 also affect the nitric oxides, adhesion molecules, cytokines and chemokines that destroy the cartilage.
In the past three decades, Interleukin-2 has been a popular object and vital for the immunotherapy of several diseases, including cancers. However, the adverse effects of taking it are fearful; IL-2 regulation and different T cell statuses are crucial to IL-2 therapies.
Interleukin-10 is an anti-inflammatory responsive cytokine. By constraining the receptor of IL-10, we can resolve the chronic viral infection; the IL-10 overpowers the immune responses by accentuating the T cells and antigen-presenting cells.
Interleukin-18 is a regulator of autoimmune diseases and cancer. It plays an indispensable role in the acute inflammation process as a member of the IL-1 family. It can collaborate with IL-12 to stimulate natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) to produce IFNγ, which might contribute to tumour immune.
In addition, it can also work very well with IL-23 to persuade the secretion of IL-17. Nevertheless, it has pros and cons impacts on the treatment of multiple conditions.
The futility of recognising own and non-own could prevail regarding orchestrating antibodies against the components of the organism autoantibodies, which could be a profound risk factor. The organism is identified by a disappointment of the traditional instrument of self-resistance, bringing about backslides against one’s cells in the insufficiency of any current infection or various reasons, distinguished as autoimmunity. The illnesses brought about by this wonder are alluded to as autoimmune diseases.
The pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases involves mainly genetic susceptivity and past infections. Concerning infections, recruitment of leukocytes into the affected tissue is observed, following in the cell activation of tissue antigen-presenting cells (APC).
Cytokines and Autoantibodies
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease defined by immune complexes produced from autoantibodies and their specific antigens accountable for clinical indication, especially arthritis, glomerulonephritis and vasculitis.
In resemblance, another autoimmune disease widely studied that includes cytokines, besides various other factors, is type 1 diabetes mellitus. This disease is characterised by pancreatic β cells destruction due to hypersensitivity reactions mediated by CD4+ TH 1 cells reactive with islet antigens, the effect of cytotoxic T lymphocyte on lysis of islet cells, and local production of cytokines, especially tnf α, IL-1, IL-21 and IFN -α. TNF-α belongs to the superfamily tumor necrosis factor alpha.
In the same way, it stands out rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic and systemic autoimmune disease described as a progressive disability on joints, particularly of the fingers, shoulders, elbows, knees and ankles, that can promote systemic consequences like cardiovascular, pulmonary and skeletal disorders. It is characterised by the production of autoantibodies, like rheumatoid factor, cytokines, chemokines, hyperplasic synovium, osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis.
Multiple sclerosis is a neurodegenerative autoimmune disease of high mortality in adults, characterised by chronic inflammation in the central nervous system with secondary demyelination due to leukocyte and cytokines infiltration of brain tissue and spinal cord. Clinical manifestations are weakness, paralysis and ocular symptoms.
At last, one more infection with cytokine support in its pathogenesis is cardiovascular failure, an ongoing sickness portrayed by cardiovascular impedance because of hypertension, dead myocardial tissue, arrhythmias, and other heart illnesses. Recent evidence showed the involvement of the adaptive immune system attacks the development and progression of heart failure, which is related to high mortality in adults.
To summarize, various types of cytokines are engaged with autoimmune diseases, which plays a significant part, particularly in the inflammatory process, and adding to the pathogenesis. Several researchers have studied the evaluation of the association between cytokines and the assessment of these sicknesses, such as anti-TNF tumor necrosis factor for rheumatoid arthritis.
To know more about our Elisa assays, please contact us now!